<<Back to Oracle ASM Main Page
What is Oracle ASM
Oracle Automatic Storage Management (ASM) is high-performance database file system and disk manager. Oracle ASM is Oracle's recommended storage management solution that provides an alternative to conventional volume managers, file systems, and raw devices. Oracle ASM uses disk groups to store data files; an Oracle ASM disk group is a collection of disks that Oracle ASM manages as a unit
ASM binaries are integrated with oracle clusterware software and therefore to configure ASM you must install oracle Grid infrastructure software ( standalone or in Clusterware mode depending on your requirement).To understand Oracle ASM you first need to understand the following concepts.
• Oracle ASM Instances
• Oracle ASM Disk Groups
• Mirroring and Failure Groups
• Oracle ASM Disks
• Oracle ASM Allocation Units
• Oracle ASM Files
• Oracle ASM Striping
Oracle ASM Instances
ASM is implemented as a special kind of Oracle instance, with its own System Global Area and background processes. The ASM instance is tightly integrated with the database instance. Every server running one or more database instances that use ASM for storage has an ASM instance. In a Real Application Clusters environment, there is one ASM instance for each node, and the ASM instances communicate with each other on a peer-to-peer basis. Only one ASM instance is required for each node regardless of the number of database instances on the node. Varios possible relationship between DB instance and ASM instance is shown below.
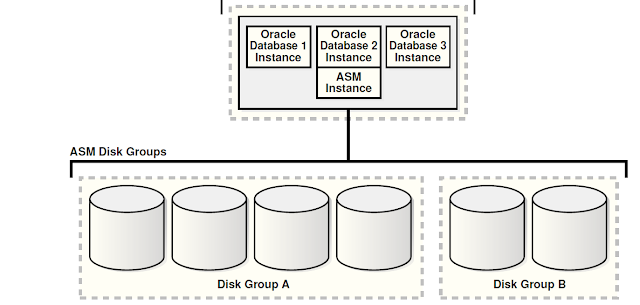
Multiple Single Instance DB on one Server.
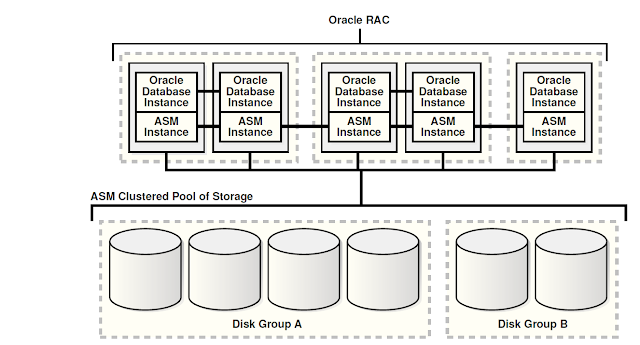
Oracle ASM Cluster Configuration with Oracle RAC
Single-Instance Databases with Clustered ASM instanceMultiple Single Instance DB on one Server.
Oracle ASM Cluster Configuration with Oracle RAC
As you may have noticed by now there is always exactly one ASM Instance per server irrespective of number of DB Instances running on that server. ASM instance may run in cluster as shown in fig 2 & 3. You can start stop ASM instance similar as DB instance. ASM instance must be running and mounting the diskgroup to start the database instance on this server.
The status of the ASM instance is always started
Oracle ASM instances manage the metadata of the disk group and provide file layout information to the database instances. Oracle ASM metadata is the information that Oracle ASM uses to control a disk group and the metadata resides within the disk group itself.Oracle ASM metadata
Oracle ASM metadata includes the following information.
• The disks that belong to a disk group
• The amount of space that is available in a disk group
• The file names of the files in a disk group
• The location of disk group data file extents
• A redo log that records information about atomically changing metadata blocks
• Oracle ADVM volume information and so on...
NOTE: If the Oracle ASM instance on a node in a Standard Oracle ASM cluster fails, then all of the database instances on that node also fail. However, in an Oracle Flex ASM configuration, Oracle 12c database instances would not fail as they would be able to access another Oracle ASM instance remotely on another node. We will discuss Oracle Flex ASM in deep in another post.• The amount of space that is available in a disk group
• The file names of the files in a disk group
• The location of disk group data file extents
• A redo log that records information about atomically changing metadata blocks
• Oracle ADVM volume information and so on...
Oracle ASM Disk Group
A disk group consists of multiple disks. A valid ASM disk could be raw partition, Logical volumes , Network-attached files (NFS) etc.
Mirroring and Failure Groups
Mirroring protects data integrity by storing copies of data on multiple disks at cost of addition storage space. When you create a disk group you specify the redundancy levels. Different diskgroups may have different redundancy levels. You can even control the redundancy at file level stored in a DG this means that you can store non mirrored and mirrored files in the same DG (DG with redundancy). The redundancy level controls how many disk failures are tolerated without dismounting the disk group or losing data. There are 3 types of redundancy
• Normal or 2-way mirroring (usable space = total space/2) this is default level when creating a DG. Minimum disk needed 2
• High for 3-way mirroring (usable space = total space/3 ) Minimum disk needed 3
• External to not use Oracle ASM mirroring, such as when you configure hardware RAID for redundancy.
• High for 3-way mirroring (usable space = total space/3 ) Minimum disk needed 3
• External to not use Oracle ASM mirroring, such as when you configure hardware RAID for redundancy.
Oracle ASM Disks
Oracle ASM disks are the storage devices that are provisioned to Oracle ASM disk groups.Examples of Oracle ASM disks include:
• A disk or partition from a storage array
• An entire disk or the partitions of a disk
• Logical volumes
• Network-attached files (NFS)
• A disk or partition from a storage array
• An entire disk or the partitions of a disk
• Logical volumes
• Network-attached files (NFS)
Oracle ASM Allocation Units
An allocation unit is the fundamental unit of allocation within a disk group.An Oracle ASM file consists of one or more file extents.A file extent consists of one or more allocation units.When you create a disk group, you can set the Oracle ASM allocation unit size with the AU_SIZE disk group attribute. The values can be 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, or 64 MB,depending on the specific disk group compatibility level. Larger AU sizes typically provide performance advantages for data warehouse applications that use large sequential reads.
Oracle ASM Files
Files that are stored in Oracle ASM disk groups are called Oracle ASM files.Each Oracle ASM file is contained within a single Oracle ASM disk group. Oracle ASM automatically generates Oracle ASM file names as part of file creation and tablespace creation. Oracle ASM file names begin with a plus sign (+) followed by a disk group name. You can specify user-friendly aliases for Oracle ASM files and create a hierarchical directory structure for the aliases.
Oracle ASM Striping
ASM striping is the process of dividing a file into chunks extents and spreading the extents evenly across all disks in the disk group.Oracle ASM striping has two primary purposes: balance loads across all of the disks in a disk group and reduce I/O latency.
There are 2 types of ASM striping
Coarse-Grained Striping
With coarse grained striping ASM writes data to each disk in the same round robin fashion, but writes chunks in the size of the ASM instance’s allocation unit (AU) size, default is 1MB.
Fine-Grained Striping
Fine striping writes 128 KB data to each ASM Disk in the diskgroup in a round robin fashion, 128 KB goes to the first disk, then the next 128 KB, goes to the next disk, etc. According to manual, The fine-grained stripe size always equals 128 KB in any configuration; this provides lower I/O latency for small I/O operations.” Small I/O operations sure sounds like a good candidate for redo logs, control files etc
Key Benefits of ASM
- Simplifies and automates storage management
- Increases storage utilization and agility
- Delivers predictable performance, availability and scalability.
- Support database failure in the event of server crash.
- Integrated storage management with ACFS



Comments
Post a Comment