Understanding ASM Disk:Diskgroup and Diskgroup Attributes
In this post I will give you a brief idea about ASM components. The post is helpful for beginners to understand the ASM and Its components
ASM Disks
To create ASM disk group you need valid ASM disks. Valid ASM disks can be
A Disk Partition
A Logical Unit Number (LUN)
A Logical Volume
A Network File System (NFS)
A Disk Partition
A Logical Unit Number (LUN)
A Logical Volume
A Network File System (NFS)
Here is an Example of Valid ASM Disk. You need correct permissions on these disks so that ASM can read them. I have ASM AFD configured in my environment and therefore the below permissions are correct for me
[root@TEST05]# ls -lrt /dev/xvd*
brw-rw---- 1 root disk 202, 64 Jun 4 12:41 /dev/xvde
brw-rw---- 1 root disk 202, 48 Jun 4 12:41 /dev/xvdd
brw-rw---- 1 root disk 202, 32 Jun 4 12:41 /dev/xvdc
brw-rw---- 1 root disk 202, 80 Jun 4 12:41 /dev/xvdf
brw-rw---- 1 root disk 202, 160 Jun 4 12:41 /dev/xvdk
brw-rw---- 1 root disk 202, 64 Jun 4 12:41 /dev/xvde
brw-rw---- 1 root disk 202, 48 Jun 4 12:41 /dev/xvdd
brw-rw---- 1 root disk 202, 32 Jun 4 12:41 /dev/xvdc
brw-rw---- 1 root disk 202, 80 Jun 4 12:41 /dev/xvdf
brw-rw---- 1 root disk 202, 160 Jun 4 12:41 /dev/xvdk
ASM Diskgroup
ASM groups the disks in Diskgroup. A disk group can have 1 or more (from 12c and later maximum 10,000 disks )disks. You can create a DG using ASMCMD/ASMCA/SQLPLUS or OEM utility.ASM Diskgroup Attributes
Disk group attributes are parameters that are bound to a disk group, rather than an Oracle ASM instance. Some disk group attributes can be set when a disk group is created or altered. Other disk attributes can only be set when a disk group is created or only be set when a disk group is alteredHow to List ASM Diskgroup Attributes
You can use asmcmd lsattr or v$asm_attribute view to display the ASM diskgroup attributes
$asmcmd lsattr <= lists all available ASM diskgroup attributes
Synopsis
lsattr [-G <diskgroup> ] [-lm] [--suppressheader] [<pattern>]
lsattr [-G <diskgroup> ] [-lm] [--suppressheader] [<pattern>]
Description
The options for the lsattr command are described below.
The options for the lsattr command are described below.
-G diskgroup - Disk group name.
-l - Display names with values.
-m - Displays additional information, such as the RO
and Sys columns.
--suppressheader - Suppresses column headings.
pattern - Display the attributes that contain pattern
expression.
-l - Display names with values.
-m - Displays additional information, such as the RO
and Sys columns.
--suppressheader - Suppresses column headings.
pattern - Display the attributes that contain pattern
expression.
Listing only the Diskgroup Attributes Having Values for a Particular DG
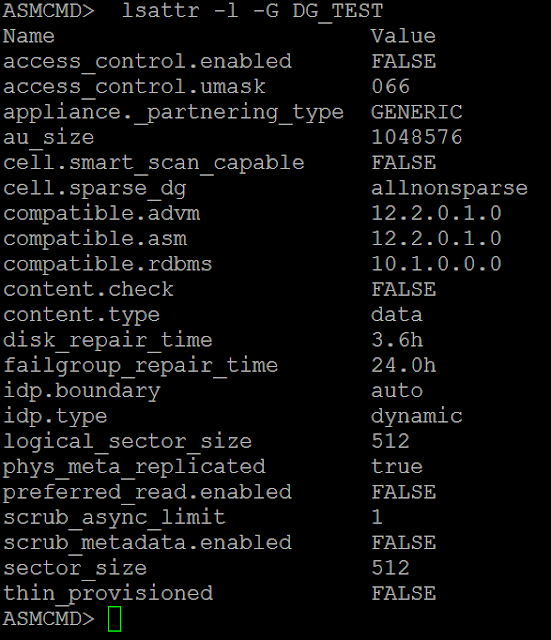
ASMCMD> lsattr -l -G DG_TEST
Apply Filter while Listing the Diskgroup Attributes
You can even apply filter to filter out only desired attributes
ASMCMD> lsattr -l -G DG_TEST scrub*
How to Configure ASM Diskgroup Attribute
You can configure the ASM diskgroup attributes either using asmcmd setattr command or alter diskgroup command from ASM Instance
Synopsis
setattr -G <diskgroup> <attribute_name> <attribute_value>
setattr -G <diskgroup> <attribute_name> <attribute_value>
Description
The options for the setattr command are described below.
The options for the setattr command are described below.
-G diskgroup - Disk group name.
attribute_name - Name of the attribute.
attribute_value - Value of the attribute.
attribute_name - Name of the attribute.
attribute_value - Value of the attribute.
ASMCMD> lsattr -l -G DG_TEST_DATA compatible*
Name Value
compatible.advm 12.2.0.1.0
compatible.asm 12.2.0.1.0
compatible.rdbms 10.1.0.0.0
ASMCMD> setattr -G DG_TEST_DATA compatible.rdbms 12.2.0.1.0
ASMCMD> lsattr -l -G DG_TEST_DATA compatible*Name Value
compatible.advm 12.2.0.1.0
compatible.asm 12.2.0.1.0
compatible.rdbms 12.2.0.1.0
Name Value
compatible.advm 12.2.0.1.0
compatible.asm 12.2.0.1.0
compatible.rdbms 10.1.0.0.0
ASMCMD> setattr -G DG_TEST_DATA compatible.rdbms 12.2.0.1.0
ASMCMD> lsattr -l -G DG_TEST_DATA compatible*Name Value
compatible.advm 12.2.0.1.0
compatible.asm 12.2.0.1.0
compatible.rdbms 12.2.0.1.0
SQL> select NAME,VALUE from v$asm_attribute where GROUP_NUMBER=1 and NAME like '%repair%';
NAME VALUE
------------------------------ ----------------------------------------
disk_repair_time 3.6h
failgroup_repair_time 24.0h
------------------------------ ----------------------------------------
disk_repair_time 3.6h
failgroup_repair_time 24.0h
SQL> alter diskgroup DG_TEST_DATA set attribute 'disk_repair_time'='5h';
Diskgroup altered.
SQL> select NAME,VALUE from v$asm_attribute where GROUP_NUMBER=1 and NAME like '%repair%';
NAME VALUE
------------------------------ ----------------------------------------
disk_repair_time 5h
failgroup_repair_time 24.0h
------------------------------ ----------------------------------------
disk_repair_time 5h
failgroup_repair_time 24.0h
ASM Instance
An ASM instance is similar to a Database Instance. It is used to mount the Diskgroup and provide the access of the diskgroup (storage) to the database. The metadata ASM uses to control the diskgroups resides in the DG itself




Thanks for sharing this knowledge.
ReplyDeleteThanks for the comment .....
Delete