<<Back to Oracle ASM Main Page
Alter Diskgroup
There are many occasions where one need to alter the Diskgroup. In this post I will show you only those which are most frequently required. You can alter a disk group with SQL*Plus, ASMCA, or ASMCMD commands.- Adding Disks to a Disk Group
- Dropping Disks from Disk Group
- Replacing Disks in Disk Group
- Renaming Disks in Disk Group
- Resizing Disks in Disk Group
- Changing Diskgroup Attributes
- Undropping Disks in Disk Group
- Creating ADVM Volumes
How to Add Disk in a Diskgroup
I have already created a DG "TEST_DG" Click Here to See How to Create ASM Diskgroup. The Diskgroup Configuration for TEST_DG is shown belowLet us find the available which we can add to TEST_DG diskgroup
$ asmcmd lsdsk --candidate -p
Group_Num Disk_Num Incarn Mount_Stat Header_Stat Mode_Stat State Path
0 0 0 CLOSED PROVISIONED ONLINE NORMAL AFD:TEST08
0 1 0 CLOSED PROVISIONED ONLINE NORMAL AFD:TEST09
I will add Disk TEST08 to TEST_DG diskgroup . Login to ASM as sysasm and execute below command
SQL> alter diskgroup TEST_DG add disk 'AFD:TEST08';
Diskgroup altered.
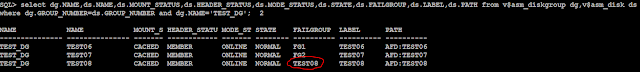
So the Diskgroup has been added successfully but as you can see the disk has been assigned a default failgroup because I have not specified any failgroup name, which is of course incorrect and I must drop this disk and add it correctly.
Note1:-Each disk is assigned to its own failure group if no failure group name specified while adding the disk or creating a diskgroup
Note2:-Adding/Dropping the Disk from a disk group triggers rebalance operation which is a performance overhead. You can check the rebalance operation status from V$ASM_OPERATION
Note3:- You can add a Disk in the Diskgroup with force option even if this disk was previously a member of a disk group that no longer exists or no longer mounted and therefore be very careful while using force because you will not be able to mount the diskgroup again if the disk was belonging a DG which was dismounted
How to Drop a Disk from ASM Disk Group
SQL> alter diskgroup test_dg drop disk TEST08;
Diskgroup altered.
How to Replace Disks in ASM Disk Group
A disk or multiple disks in a disk group can be replaced, rather than dropped and added back
Compatible.asm should be 12.1.0.0.0 or higher.
I lost the disk TEST06 which I replaced with good available disk TEST08 instead of dropping and adding the disk
SQL> alter diskgroup TEST_DG replace disk TEST06 with 'AFD:TEST08';
Diskgroup altered.
How to Rename a Disk in a Disk Group
SQL> alter diskgroup TEST_DG rename disk 'TEST06' to 'TEST08';
alter diskgroup TEST_DG rename disk 'TEST06' to 'TEST08'
*
ERROR at line 1:
alter diskgroup TEST_DG rename disk 'TEST06' to 'TEST08'
*
ERROR at line 1:
ORA-31020: The operation is not allowed, Reason: disk group is NOT mounted in RESTRICTED state.
SQL> alter diskgroup TEST_DG dismount;
Diskgroup altered.
SQL> alter diskgroup TEST_DG mount restricted;
Diskgroup altered.
SQL> alter diskgroup TEST_DG rename disk 'TEST06' to 'TEST08';
Diskgroup altered.
Note4:- Diskgroups mounted in restricted mode are not available to the Database and therefore operation involves downtime
How to Resize Disk in Disk Group
Note5:-When resizing disks in a disk group, all the disks must be of equal size
SQL> alter diskgroup TEST_DG resize all size 1G;
Diskgroup altered.
How to Change Diskgroup Attributes
SQL> select NAME,VALUE from v$asm_attribute where GROUP_NUMBER='4' and NAME like '%compa%';NAME VALUE
-------------------------------------------------- ------------------------------
compatible.asm 11.2.0.2.0
compatible.rdbms 10.1.0.0.0
compatible.advm 11.2.0.2.0
SQL> alter diskgroup TEST_DG set attribute 'compatible.asm'='12.2.0.0';
Diskgroup altered.
SQL> select NAME,VALUE from v$asm_attribute where GROUP_NUMBER='4' and NAME like '%compa%';
NAME VALUE
-------------------------------------------------- ------------------------------
compatible.asm 12.2.0.0.0
compatible.rdbms 10.1.0.0.0
compatible.advm 11.2.0.2.0
How to Undrop Disks in Diskgroup
The UNDROP DISKS clause of the ALTER DISKGROUP statement enables you to cancel all pending drops of disks within disk groups.
If a drop disk operation has completed, then this statement cannot be used to restore it. This statement cannot be used to restore disks that are being dropped as the result of a DROP DISKGROUP statement, or for disks that are being dropped using the FORCE clause.
If a drop disk operation has completed, then this statement cannot be used to restore it. This statement cannot be used to restore disks that are being dropped as the result of a DROP DISKGROUP statement, or for disks that are being dropped using the FORCE clause.
SQL> select dg.NAME,ds.NAME,ds.MOUNT_STATUS,ds.HEADER_STATUS,ds.MODE_STATUS,ds.STATE,ds.FAILGROUP,ds.LABEL,ds.PATH from v$asm_diskgroup dg,v$asm_disk ds
where dg.GROUP_NUMBER=ds.GROUP_NUMBER and dg.NAME='TEST_DG';
where dg.GROUP_NUMBER=ds.GROUP_NUMBER and dg.NAME='TEST_DG';
NAME NAME MOUNT_S HEADER_STATU MODE_ST STATE FAILGROUP LABEL PATH
--------------- --------------- ------- ------------ ------- -------- ---------- ---------- ----------
TEST_DG TEST06 CACHED MEMBER ONLINE NORMAL TEST06 TEST06 AFD:TEST06
TEST_DG TEST07 CACHED MEMBER ONLINE NORMAL TEST07 TEST07 AFD:TEST07
TEST_DG TEST08 CACHED MEMBER ONLINE NORMAL TEST08 TEST08 AFD:TEST08
TEST_DG TEST09 CACHED MEMBER ONLINE NORMAL TEST09 TEST09 AFD:TEST09
--------------- --------------- ------- ------------ ------- -------- ---------- ---------- ----------
TEST_DG TEST06 CACHED MEMBER ONLINE NORMAL TEST06 TEST06 AFD:TEST06
TEST_DG TEST07 CACHED MEMBER ONLINE NORMAL TEST07 TEST07 AFD:TEST07
TEST_DG TEST08 CACHED MEMBER ONLINE NORMAL TEST08 TEST08 AFD:TEST08
TEST_DG TEST09 CACHED MEMBER ONLINE NORMAL TEST09 TEST09 AFD:TEST09
I have 4 Disks in my Diskgroup TEST_DG and I wanted to test the undrop functionality by dropping and undropping disk TEST07
SQL> ALTER DISKGROUP TEST_DG DROP DISK 'TEST07';
Diskgroup altered.
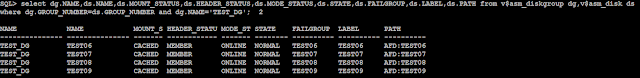
SQL> select dg.NAME,ds.NAME,ds.MOUNT_STATUS,ds.HEADER_STATUS,ds.MODE_STATUS,ds.STATE,ds.FAILGROUP,ds.LABEL,ds.PATH from v$asm_diskgroup dg,v$asm_disk ds
where dg.GROUP_NUMBER=ds.GROUP_NUMBER and dg.NAME='TEST_DG';
where dg.GROUP_NUMBER=ds.GROUP_NUMBER and dg.NAME='TEST_DG';
NAME NAME MOUNT_S HEADER_STATU MODE_ST STATE FAILGROUP LABEL PATH
--------------- --------------- ------- ------------ ------- -------- ---------- ---------- ----------
TEST_DG TEST06 CACHED MEMBER ONLINE NORMAL TEST06 TEST06 AFD:TEST06
TEST_DG TEST07 CACHED MEMBER ONLINE DROPPING TEST07 TEST07 AFD:TEST07
TEST_DG TEST08 CACHED MEMBER ONLINE NORMAL TEST08 TEST08 AFD:TEST08
TEST_DG TEST09 CACHED MEMBER ONLINE NORMAL TEST09 TEST09 AFD:TEST09
--------------- --------------- ------- ------------ ------- -------- ---------- ---------- ----------
TEST_DG TEST06 CACHED MEMBER ONLINE NORMAL TEST06 TEST06 AFD:TEST06
TEST_DG TEST07 CACHED MEMBER ONLINE DROPPING TEST07 TEST07 AFD:TEST07
TEST_DG TEST08 CACHED MEMBER ONLINE NORMAL TEST08 TEST08 AFD:TEST08
TEST_DG TEST09 CACHED MEMBER ONLINE NORMAL TEST09 TEST09 AFD:TEST09
At this point as you can see the disk is in dropping status and not yet dropped. The data stored in the disk is being relocated to other available disks and we can check the details about the same by querying v$asm_operation view.
As long as the disk is not dropped we can undrop it
SQL> select * from v$asm_operation;
GROUP_NUMBER OPERA PASS STAT POWER ACTUAL SOFAR EST_WORK EST_RATE EST_MINUTES ERROR_CODE CON_ID
------------ ----- --------- ---- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ----------- -------------------------------------------- ----------
4 REBAL COMPACT WAIT 1 1 0 0 0 0 0
4 REBAL REBALANCE RUN 1 1 72 3059 1388 2 0
4 REBAL REBUILD DONE 1 1 0 0 0 0 0
4 REBAL RESYNC DONE 1 1 0 0 0 0 0
------------ ----- --------- ---- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ----------- -------------------------------------------- ----------
4 REBAL COMPACT WAIT 1 1 0 0 0 0 0
4 REBAL REBALANCE RUN 1 1 72 3059 1388 2 0
4 REBAL REBUILD DONE 1 1 0 0 0 0 0
4 REBAL RESYNC DONE 1 1 0 0 0 0 0
SQL> ALTER DISKGROUP TEST_DG UNDROP DISKS;
Diskgroup altered.
SQL> select dg.NAME,ds.NAME,ds.MOUNT_STATUS,ds.HEADER_STATUS,ds.MODE_STATUS,ds.STATE,ds.FAILGROUP,ds.LABEL,ds.PATH from v$asm_diskgroup dg,v$asm_disk ds
where dg.GROUP_NUMBER=ds.GROUP_NUMBER and dg.NAME='TEST_DG';
where dg.GROUP_NUMBER=ds.GROUP_NUMBER and dg.NAME='TEST_DG';
NAME NAME MOUNT_S HEADER_STATU MODE_ST STATE FAILGROUP LABEL PATH
--------------- --------------- ------- ------------ ------- -------- ---------- ---------- ----------
TEST_DG TEST06 CACHED MEMBER ONLINE NORMAL TEST06 TEST06 AFD:TEST06
TEST_DG TEST07 CACHED MEMBER ONLINE NORMAL TEST07 TEST07 AFD:TEST07
TEST_DG TEST08 CACHED MEMBER ONLINE NORMAL TEST08 TEST08 AFD:TEST08
TEST_DG TEST09 CACHED MEMBER ONLINE NORMAL TEST09 TEST09 AFD:TEST09
--------------- --------------- ------- ------------ ------- -------- ---------- ---------- ----------
TEST_DG TEST06 CACHED MEMBER ONLINE NORMAL TEST06 TEST06 AFD:TEST06
TEST_DG TEST07 CACHED MEMBER ONLINE NORMAL TEST07 TEST07 AFD:TEST07
TEST_DG TEST08 CACHED MEMBER ONLINE NORMAL TEST08 TEST08 AFD:TEST08
TEST_DG TEST09 CACHED MEMBER ONLINE NORMAL TEST09 TEST09 AFD:TEST09
And as you can see the disk status is again normal and not dropping any more.
SQL> select * from v$asm_operation;
GROUP_NUMBER OPERA PASS STAT POWER ACTUAL SOFAR EST_WORK EST_RATE EST_MINUTES ERROR_CODE CON_ID
------------ ----- --------- ---- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ----------- -------------------------------------------- ----------
4 REBAL COMPACT WAIT 1 1 0 0 0 0 0
4 REBAL REBALANCE RUN 1 1 242 2298 927 2 0
4 REBAL REBUILD DONE 1 1 0 0 0 0 0
4 REBAL RESYNC DONE 1 1 0 0 0 0 0
------------ ----- --------- ---- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ----------- -------------------------------------------- ----------
4 REBAL COMPACT WAIT 1 1 0 0 0 0 0
4 REBAL REBALANCE RUN 1 1 242 2298 927 2 0
4 REBAL REBUILD DONE 1 1 0 0 0 0 0
4 REBAL RESYNC DONE 1 1 0 0 0 0 0
How to Create ADVM (ASM Dynamic Volume Manager) Volume in Diskgroup
SQL> alter diskgroup TEST_DG add volume vol1 size 2G;
Diskgroup altered.
Once you have created the Volume you can mount it on OS level and you can use it as regular mount pointDiskgroup altered.
$mkfs -t acfs /dev/asm/vol1-467
As root user
#mount -t acfs /dev/asm/vol1-467 /acfs_test




















Comments
Post a Comment