<<Back to PT Main Page
Steps to Configure HugePages on Linux 64-bit for Oracle Database
Step0: Check if Transparent HugePages are enabledcat /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled
[always] madvise never
Starting from RHEL6/OL6, Transparent HugePages are implemented and enabled by default. Therefore Oracle recommends disabling Transparent HugePages on all servers running Oracle databases this MOS note (Doc ID 1557478.1)
Step1: Verify the current OS Page Size
#grep Hugepagesize /proc/meminfo
oracle soft memlock 419430400
oracle hard memlock 419430400
NOTE: There is no harm in setting this value larger than your SGA requirements.
Step3: Verify the memlock limit
Re-logon to the Oracle product owner account (e.g. 'oracle') and check the memlock limit
#ulimit -l
419430400
Step4: AMM if already Configured
Disable Automatic Memory Management (AMM) Feature (if already enabled)
SQL>create pfile from spfile;
SQL>alter system set MEMORY_TARGET=0 sope=spfile;
SQL>alter system set MEMORY_MAX_TARGET=0 sope=spfile;
Step5: Calculate Number of HugePages
calculate the recommended value for the vm.nr_hugepageskernel parameter. I calculated the following value for 400GB of SGA.
kernel.shmmax=429496729600
vm.nr_hugepages=204800
vm.hugetlb_shm_group=<gid of dba group>
This is how you calculate the parameter value used in step2 & 5
#grep Hugepagesize /proc/meminfo
Step2:Configure memlock
Set the memlock user limit in /etc/security/limits.conf file. Set the value (in KB) slightly smaller than installed RAM. e.g. If you have 450GB RAM installed, you may set:oracle soft memlock 419430400
oracle hard memlock 419430400
NOTE: There is no harm in setting this value larger than your SGA requirements.
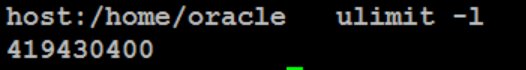
Step3: Verify the memlock limit
Re-logon to the Oracle product owner account (e.g. 'oracle') and check the memlock limit
#ulimit -l
419430400
Step4: AMM if already Configured
Disable Automatic Memory Management (AMM) Feature (if already enabled)
SQL>create pfile from spfile;
SQL>alter system set MEMORY_TARGET=0 sope=spfile;
SQL>alter system set MEMORY_MAX_TARGET=0 sope=spfile;
Step5: Calculate Number of HugePages
calculate the recommended value for the vm.nr_hugepageskernel parameter. I calculated the following value for 400GB of SGA.
kernel.shmmax=429496729600
vm.nr_hugepages=204800
vm.hugetlb_shm_group=<gid of dba group>
This is how you calculate the parameter value used in step2 & 5
kernel.shmmax = 429496729600 # 1024 * 1024 * 1024 * 400
kernel.shmall = 117964800 # use formula echo "450 * 1024^3 / 4096" | bc
The number of HugePages = shmmax [in KB] / page size [in KB].
Step6:Adopt the parameter value in /etc/sysctl.conf file
Edit the file /etc/sysctl.conf and set the
kernel.shmmax=429496729600
vm.nr_hugepages=204800
vm.hugetlb_shm_group=3500
Step7: Set the desired SGA size
Step8: Adopt kernel.shmall /etc/sysctl.conf
Set SHMALL equal to the sum of all the SGAs on the system, divided by the page size.
kernel.shmall = 483183820800
If this parameter not sized properly you will encounter following error while starting up the database instance
ORA-27102: out of memory Linux-X86_64 Error: 28: No space left on device
Step9: Restart the Server and Database
Why Use HugePage ?:
By default Linux Kernel manages the memory with 4K Page size, With hugePages you can increase the page size. As you see I configured it 2MB.
You can configure the page size up to 1G if supported by the hardware.
Now Linux kernel maintains the page table to manage the pages. Smaller page size increases the page numbers resulting larger page tables, which requires more memory & pointers to store and manage those pages and hence reducing the overall performance.
With larger page size you got less pages , resulting smaller page table and in tern better overall performance
When Use HugePages?
In general and to my experience if you have SGA>16G you should use HugePages and you will benefit the performance benefits. Oracle suggests using huge pages starting with 8G SGA itself.
Where can we Use HugePages?
All Linux/Unix Platform. Not sure about windows
Edit the file /etc/sysctl.conf and set the
kernel.shmmax=429496729600
vm.nr_hugepages=204800
vm.hugetlb_shm_group=3500
Step7: Set the desired SGA size
Set SHMALL equal to the sum of all the SGAs on the system, divided by the page size.
kernel.shmall = 483183820800
If this parameter not sized properly you will encounter following error while starting up the database instance
ORA-27102: out of memory Linux-X86_64 Error: 28: No space left on device
Step9: Restart the Server and Database
- Stop Database
- Restart the server
- Start the database
Step10: Validate the HugePage Configuration
#grep HugePages /proc/meminfo
AnonHugePages: 155648 kB
HugePages_Total: 209920
HugePages_Free: 199991
HugePages_Rsvd: 194872
HugePages_Surp: 0
Database Aletlog will also display the usages of Huge Pages
HugePages_Total: 209920
HugePages_Free: 199991
HugePages_Rsvd: 194872
HugePages_Surp: 0
Database Aletlog will also display the usages of Huge Pages
Starting ORACLE instance (normal)
************************ Large Pages Information *******************
Per process system memlock (soft) limit = 410 GB
Total Shared Global Region in Large Pages = 400 GB (100%)
Large Pages used by this instance: 204801 (400 GB)
Large Pages unused system wide = 5119 (10 GB)
Large Pages configured system wide = 209920 (410 GB)
Large Page size = 2048 KB
************************ Large Pages Information *******************
Per process system memlock (soft) limit = 410 GB
Total Shared Global Region in Large Pages = 400 GB (100%)
Large Pages used by this instance: 204801 (400 GB)
Large Pages unused system wide = 5119 (10 GB)
Large Pages configured system wide = 209920 (410 GB)
Large Page size = 2048 KB
Why Use HugePage ?:
By default Linux Kernel manages the memory with 4K Page size, With hugePages you can increase the page size. As you see I configured it 2MB.
You can configure the page size up to 1G if supported by the hardware.
Now Linux kernel maintains the page table to manage the pages. Smaller page size increases the page numbers resulting larger page tables, which requires more memory & pointers to store and manage those pages and hence reducing the overall performance.
With larger page size you got less pages , resulting smaller page table and in tern better overall performance
When Use HugePages?
In general and to my experience if you have SGA>16G you should use HugePages and you will benefit the performance benefits. Oracle suggests using huge pages starting with 8G SGA itself.
Where can we Use HugePages?
All Linux/Unix Platform. Not sure about windows




Comments
Post a Comment